What is Anti-Money Laundering (AML)?
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) refers to the regulations, laws, and procedures implemented to prevent criminals from disguising illegally obtained funds as legitimate income.
AML regulations for real estate in the UAE are designed to prevent and detect money laundering and terrorist financing activities. Brokers, real estate agents, lawyers, notaries, and independent accountants involved in real estate transactions must follow certain rules under the AML-CFT Law. These include:
- Identifying and assessing ML/FT risks
- Establishing, documenting, and updating policies and procedures to mitigate the identified ML/FT risks
- Maintaining adequate risk-based customer due diligence (CDD) and ongoing monitoring procedures
- Identifying and reporting suspicious transactions
- Implementing an adequate governance framework for AML/CFT, including appointing an AML/CFT Compliance Officer
The UAE has established a robust AML framework under the Federal Law on Anti-Money Laundering and Counter-Terrorism Financing, in line with international standards set by the Financial Action Task Force (FATF).
Anti-Money Laundering and Combating the Financing of Terrorism and Illegal Organizations Guidelines for Designated Non – Financial Businesses and Professions (DNFBP) are applicable to Real estate agents and brokers.

AML/TF Policy – Internal Control System
AML/TF Policy provides a structured approach to identifying, managing, and mitigating the risks associated with money laundering and terrorist financing. Here are the key reasons why having an internal AML policy is essential:
1. Regulatory Compliance
- Ensure adherence to local and international laws.
- Aligns operations with regulatory frameworks.
- An internal AML policy demonstrates a proactive approach to compliance.
2. Risk Management
- Ensures high-risk customers are subject to enhanced scrutiny.
- Prevents involvement in financial scandals or criminal investigations that can severely damage the businessʼs reputation and operational continuity.
3. Legal Protection
- Protects the business from the financial and legal consequences of failing to comply with AML regulations.
- Ensures that employees are aware of their responsibilities and are protected when they report suspicious activities in good faith.
Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
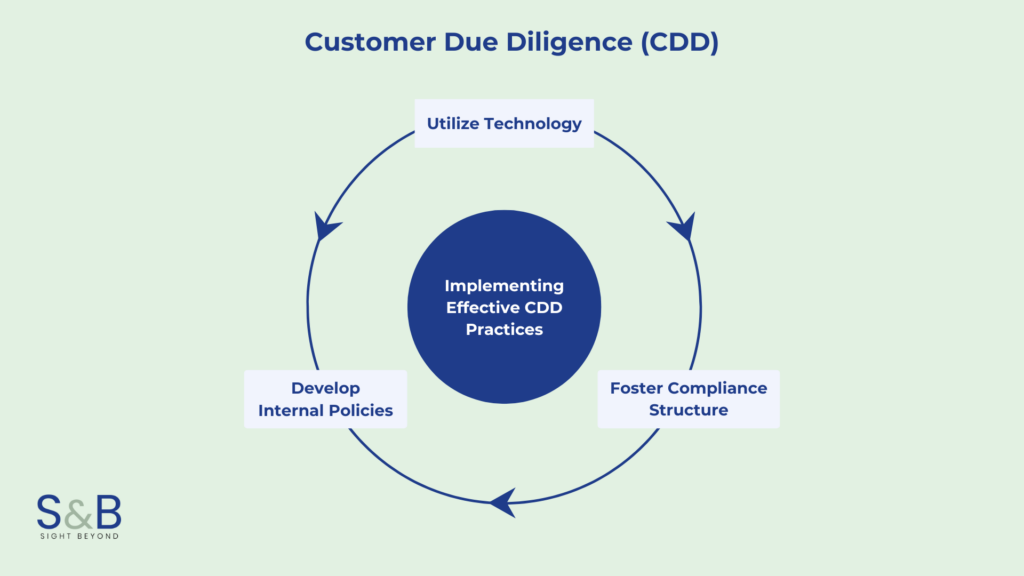
Main Elements of a Customer Due Diligence Program
- Customer Identification – Collecting and Verifying basic information of customer.
- Profiles – Establish a risk profile for their customers, commensurate with the types
and levels of risk involved - Customer Acceptance– To determine whether to accept a customer based on the risk they pose.
- Risk Rating -To assess and categorize the level of risk associated with each customer.
- Monitoring – To continuously monitor customer transactions and activities to detect
unusual or suspicious behavior. - Investigation – To investigate and address any suspicious activities identified through
monitoring - Documentation -To maintain comprehensive records of all CDD processes and
decisions.
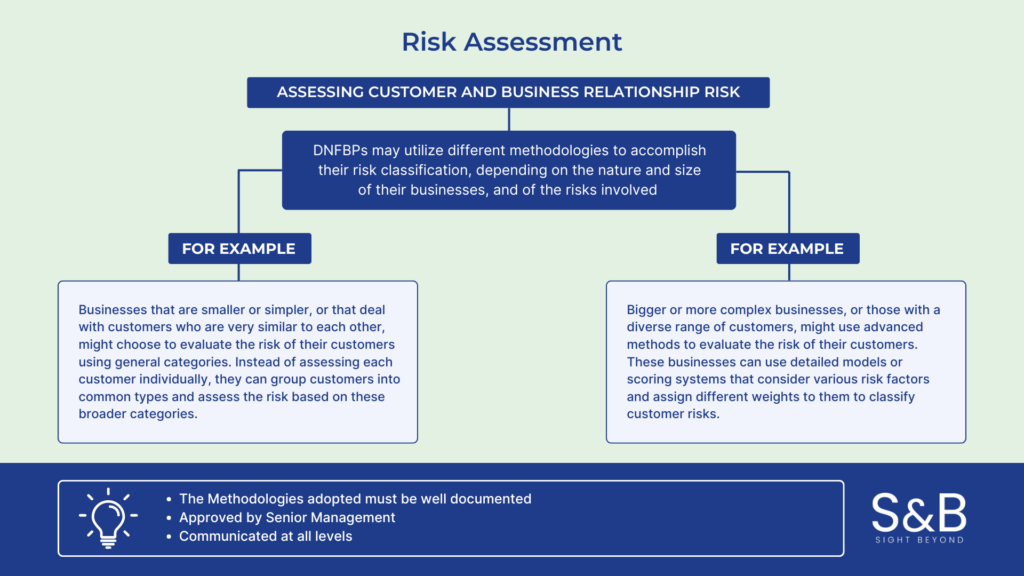
Risk Assessment
KYC Verification
| Stages | Information |
| Customer Onboarding | Collect basic customer information (name, address, date of birth, etc.) |
| If the buyer or seller are natural person(s), identification documents must include – | Obtain Valid Emirates ID or Passport copy. |
| If the buyer or seller are legal person(s), identification documents must include | Trade License; – Articles of Association; – Register of Beneficial Owners; – Emirates ID or passport copy for all Beneficial Owners; and – Emirates ID or passport copy for all shareholders/partners. |
| Verify from External Sources | Screen against sanctions lists, PEP (Politically Exposed Persons) lists, and adverse media. |
| Record Keeping | Keep records of all documents and information related to the above transactions for a minimum period of 5 years. |
| Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) for High-Risk Customers | If the customer is deemed high-risk, collect additional detailed information and perform more thorough checks. |
| Ongoing Monitoring | Continuously monitor customer transactions and update risk profiles as necessary. |
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD)
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) is a deeper and more thorough investigation process compared to standard due diligence, especially when dealing with higher-risk situations or entities. The main elements typically include:
Main elements of an enhanced due diligence program:
- Source of funds (revenue) and source of wealth;
- Identifying information on individuals with control over the customer (legal person or arrangement), such as signatories or guarantors;
- Occupation or type of business;
- Financial statements;
- Banking references;
- Domicile;
- Description of the customer’s primary trade area and whether international transactions are expected to be routine;
- Description of the business operations, the anticipated volume of currency and total sales, and a list of major customers and suppliers; and
- Explanations for changes in business activity.
Suspicious Event Where EDD May Apply:
An illogical reason for a foreign customer’s or Beneficial Owner’s presence, or establishment of a Business Relationship, in the UAE.
Importance of AML – Real Estate Sector

Reporting Requirement – Real Estate Activity Report “REAR”
Real estate brokers and agents licensed in the United Arab Emirates. The Ministry of Economy instructs all real estate brokers and agents to undertake the following procedures:
| Cash Transaction | Virtual Transaction |
| At the time of purchase/sale of freehold real estate in any emirate, and the total amount of the transaction involves physical cash equal to or more than AED 55,000 whether the cash is for the entire property or just part of its value: – Obtain and record identification documents (Emirates ID, or Passport copy). – Obtain and record receipts, invoices, contracts and Purchase & Sale Agreement. | At the time of purchase/sale of freehold real estate and using virtual assets (like cryptocurrency) to pay for part or all of the property: – Obtain and record identification documents (Emirates ID, or Passport copy). – Obtain and record receipts, invoices, contracts and Purchase & Sale Agreement. |
| Reporting | Reporting |
| Submit a ‘Real Estate Transaction Report’ (“REAR”) via the Financial Intelligence Unit’s (“FIU”) go AML platform. | Submit a ‘Real Estate Transaction Report’ (“REAR”) via the Financial Intelligence Unit’s (“FIU”) go AML platform. |
Reporting Requirement
| Type of Report | Time of Reporting |
| Suspicious Transaction Report (STR) | If, during the establishment or course of the customer relationship, or when conducting transactions on behalf of a customer or a potential customer, a reporting entity suspects transactions related to money laundering, fraud or terrorist financing. The entity should submit a SAR to the FIU at the earliest. |
| Suspicious Activity Report (SAR) | If, during the establishment or course of the customer relationship, a reporting entity suspects any activity or an attempted transaction (i.e. a non-executed transaction) that can be related to money laundering, fraud or terrorist financing. The entity should submit a SAR to the FIU at the earliest. |
| Funds Freeze Report (FFR) | Reporting entities are supposed to file Funds Freeze Report to report any freezing measure, prohibition to provide funds or services, and any attempted transactions related to ‘confirmed matches.’ |
| Partial Name Match Report (PNMR) | Reporting entities are supposed to submit Partial Name Match Report (PNMR) for any ‘potential match.’ |
| High Risk Country Report (HRC) | A reporting entity identifies transactions related to high risk countries as defined by the National Anti-Money Laundering and Combating the Financing of Terrorism and financing of Illegal Organizations Committee, then the entity should submit an HRC to the FIU. Such reported transaction(s) may only be executed three working days after reporting such to the FIU, and if the FIU does not object to conducting the transaction within the set period. |
| High Risk Country Activity Report (HRCA) | A reporting entity identifies activities related to high risk countries as defined by the National Anti-Money Laundering and Combating the Financing of Terrorism and financing of Illegal Organizations Committee. The entity should submit an HRC to the FIU. Such reported activity(ies) may only be executed three working days after reporting such to the FIU, and if the FIU does not object to conducting the activity within the set period. |
Failure to report
Failure to – immediately – report a suspicious transaction, whether intentionally or by gross negligence, is a federal crime.
Any person, including real estate agents/brokers or their managers and employees, who fails to perform their statutory obligation to report a suspicion of money laundering, or the financing of terrorism or of illegal organizations, is liable to a fine of no less than AED 100,000 and no more than AED 1,000,000 and/or imprisonment.
DO’s and DON’T’s FOR AML/TF – Real Estate Sector

How Can We Help You- AML Compliances

Conclusion
In conclusion, as real estate agents and brokers operating in the UAE, it is essential to recognize and actively manage the risks associated with money laundering (ML) and the financing of terrorism (TF). The real estate sector, given its high-value transactions and complex ownership structures, is a prime target for illicit activities. Therefore, maintaining rigorous anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorist financing (CTF) practices is not just a regulatory obligation but a fundamental component of ethical business conduct.
By adhering to these practices, you not only protect your business from potential legal and reputational risks but also play a vital role in enhancing the integrity and transparency of the UAE’s real estate market.
Thank you for your attention, and we encourage you to implement these best practices and continue to seek further training and resources to stay ahead in the fight against financial crime.
For expert guidance and comprehensive AML and CTF compliance services in the UAE, visit S&B Consulting. Let us help you safeguard your business and navigate regulatory challenges with confidence and ease.


